- Research Article
- Open access
- Published:
Robust Sparse Component Analysis Based on a Generalized Hough Transform
EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing volume 2007, Article number: 052105 (2006)
Abstract
An algorithm called Hough SCA is presented for recovering the matrix in
in , where
, where is a multivariate observed signal, possibly is of lower dimension than the unknown sources
is a multivariate observed signal, possibly is of lower dimension than the unknown sources . They are assumed to be sparse in the sense that at every time instant
. They are assumed to be sparse in the sense that at every time instant ,
, has fewer nonzero elements than the dimension of
has fewer nonzero elements than the dimension of . The presented algorithm performs a global search for hyperplane clusters within the mixture space by gathering possible hyperplane parameters within a Hough accumulator tensor. This renders the algorithm immune to the many local minima typically exhibited by the corresponding cost function. In contrast to previous approaches, Hough SCA is linear in the sample number and independent of the source dimension as well as robust against noise and outliers. Experiments demonstrate the flexibility of the proposed algorithm.
. The presented algorithm performs a global search for hyperplane clusters within the mixture space by gathering possible hyperplane parameters within a Hough accumulator tensor. This renders the algorithm immune to the many local minima typically exhibited by the corresponding cost function. In contrast to previous approaches, Hough SCA is linear in the sample number and independent of the source dimension as well as robust against noise and outliers. Experiments demonstrate the flexibility of the proposed algorithm.
References
Ballard DH: Generalizing the Hough transform to detect arbitrary shapes. Pattern Recognition 1981,13(2):111–122. 10.1016/0031-3203(81)90009-1
Ballester P: Applications of the Hough transform. In Astronomical Data Analysis Software and Systems III, ASP Conference Series Edited by: Barnes J, Crabtree DR, Hanisch RJ. 1994., 61:
Barbarossa S: Analysis of multicomponent LFM signals by a combined Wigner-Hough transform. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 1995,43(6):1511–1515. 10.1109/78.388866
Bradley PS, Mangasarian OL:
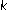 -plane clustering. Journal of Global Optimization 2000,16(1):23–32. 10.1023/A:1008324625522
-plane clustering. Journal of Global Optimization 2000,16(1):23–32. 10.1023/A:1008324625522Chen SS, Donoho DL, Saunders MA: Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM Journal of Scientific Computing 1998,20(1):33–61. 10.1137/S1064827596304010
Cichocki A, Amari S: Adaptive Blind Signal and Image Processing. John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, USA; 2002.
Cirillo L, Zoubir A, Amin M: Direction finding of nonstationary signals using a time-frequency Hough transform. Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP '05), March 2005, Philadelphia, Pa, USA 2718–2721.
Comon P: Independent component analysis. A new concept? Signal Processing 1994,36(3):287–314. 10.1016/0165-1684(94)90029-9
Donoho DL, Elad M:Optimally sparse representation in general (nonorthogonal) dictionaries via
 minimization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2003,100(5):2197–2202. 10.1073/pnas.0437847100
minimization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2003,100(5):2197–2202. 10.1073/pnas.0437847100Duda RO, Hart PE: Use of the Hough transformation to detect lines and curves in pictures. Communications of the ACM 1972,15(1):204–208.
Dudley RDepartment of Mathematics, MIT, course 18.465, 2005
Eriksson J, Koivunen V: Identifiability and separability of linear ica models revisited. Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Independent Component Analysis and Blind Source Separation (ICA '03), April 2003, Nara, Japan 23–27.
Georgiev P, Pardalos P, Theis FJ, Cichocki A, Bakardjian H: Sparse component analysis: a new tool for data mining. In Data Mining in Biomedicine. Springer, New York, NY, USA; 2005. in print
Georgiev P, Theis FJ, Cichocki A: Optimization algorithms for sparse representations and applications. In Multiscale Optimization Methods. Edited by: Pardalos P. Springer, New York, NY, USA; 2005.
Georgiev P, Theis FJ, Cichocki A: Sparse component analysis and blind source separation of underdetermined mixtures. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 2005,16(4):992–996. 10.1109/TNN.2005.849840
Goldenshluger A, Zeevi A: The Hough transform estimator. Annals of Statistics 2004,32(5):1908–1932. 10.1214/009053604000000760
Hough PVC: Machine analysis of bubble chamber pictures. In International Conference on High Energy Accelerators and Instrumentation, 1959, Geneva, Switzerland. CERN; 554–556.
Hyvärinen A, Karhunen J, Oja E: Independent Component Analysis. John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, USA; 2001.
Hyvärinen A, Oja E: A fast fixed-point algorithm for independent component analysis. Neural Computation 1997,9(7):1483–1492. 10.1162/neco.1997.9.7.1483
Lee T-W, Lewicki MS, Girolami M, Sejnowski TJ: Blind source separation of more sources than mixtures using overcomplete representations. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 1999,6(4):87–90. 10.1109/97.752062
Lin JK, Grier DG, Cowan JD: Feature extraction approach to blind source separation. Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Neural Networks for Signal Processing (NNSP '97), September 1997, Amelia Island, Fla, USA 398–405.
Rousseeuw PJ, Leroy AM: Robust Regression and Outlier Detection. John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, USA; 1987.
Shindo H, Hirai Y: An approach to overcomplete-blind source separation using geometric structure. In Proceedings of Annual Conference of Japanese Neural Network Society (JNNS '01), 2001, Nara, Japan. Naramachi Center; 95–96.
Theis FJ: A new concept for separability problems in blind source separation. Neural Computation 2004,16(9):1827–1850. 10.1162/0899766041336404
Theis FJ, García GA: On the use of sparse signal decomposition in the analysis of multi-channel surface electromyograms. Signal Processing 2006,86(3):603–623. 10.1016/j.sigpro.2005.05.032
Theis FJ, Georgiev P, Cichocki A: Robust overcomplete matrix recovery for sparse sources using a generalized Hough transform. Proceedings of 12th European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks (ESANN '04), April 2004, Bruges, Belgium 343–348. d-side, Evere, Belgium
Theis FJ, Lang EW, Puntonet CG: A geometric algorithm for overcomplete linear ICA. Neurocomputing 2004,56(1–4):381–398.
Theis FJ, Puntonet CG, Lang EW: Median-based clustering for underdetermined blind signal processing. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 2006,13(2):96–99.
Waheed K, Salem F: Algebraic overcomplete independent component analysis. Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Independent Component Analysis and Blind Source Separation (ICA '03), April 2003, Nara, Japan 1077–1082.
Zibulevsky M, Pearlmutter BA: Blind source separation by sparse decomposition in a signal dictionary. Neural Computation 2001,13(4):863–882. 10.1162/089976601300014385
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Theis, F.J., Georgiev, P. & Cichocki, A. Robust Sparse Component Analysis Based on a Generalized Hough Transform. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2007, 052105 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/52105
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/52105
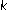 -plane clustering. Journal of Global Optimization 2000,16(1):23–32. 10.1023/A:1008324625522
-plane clustering. Journal of Global Optimization 2000,16(1):23–32. 10.1023/A:1008324625522 minimization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2003,100(5):2197–2202. 10.1073/pnas.0437847100
minimization. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2003,100(5):2197–2202. 10.1073/pnas.0437847100