- Research Article
- Open access
- Published:
Efficient Fast Stereo Acoustic Echo Cancellation Based on Pairwise Optimal Weight Realization Technique
EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing volume 2006, Article number: 084797 (2006)
Abstract
In stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation (SAEC) problem, fast and accurate tracking of echo path is strongly required for stable echo cancellation. In this paper, we propose a class of efficient fast SAEC schemes with linear computational complexity (with respect to filter length). The proposed schemes are based on pairwise optimal weight realization (POWER) technique, thus realizing a "best" strategy (in the sense of pairwise and worst-case optimization) to use multiple-state information obtained by preprocessing. Numerical examples demonstrate that the proposed schemes significantly improve the convergence behavior compared with conventional methods in terms of system mismatch as well as echo return loss enhancement (ERLE).
References
Fujii T, Shimada S: A note on multi-channel echo cancellers. CS84-178, IEICE, January 1985, in Japanese
Sondhi MM, Morgan DR: Acoustic echo cancellation for stereophonic teleconferencing. Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (ASSP '91), October 1991 141–142.
Sondhi MM, Morgan DR, Hall JL: Stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation—an overview of the fundamental problem. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 1995, 2(8):148–151. 10.1109/97.404129
Benesty J, Amand F, Gilloire A, Grenier Y: Adaptive filtering algorithms for stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation. Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP '95), May 1995, Detroit, Mich, USA 5: 3099–3102.
Benesty J, Morgan DR, Sondhi MM: A better understanding and an improved solution to the specific problems of stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing 1998, 6(2):156–165. 10.1109/89.661474
Gänsler T, Benesty J: Stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation and two-channel adaptive filtering: an overview. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing 2000, 14(6):565–586. 10.1002/1099-1115(200009)14:6<565::AID-ACS604>3.0.CO;2-2
Gay SL, Benesty J (Eds): Acoustic Signal Processing for Telecommunication. Kluwer Academic, Boston, Mass, USA; 2000.
Eneroth P, Gay SL, Gänsler T, Benesty J: A real-time implementation of a stereophonic acoustic echo canceler. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing 2001, 9(5):513–523. 10.1109/89.928916
Gänsler T, Benesty J: Multichannel acoustic echo cancellation: what's new? Proceedings of the 7th International Workshop on Acoustic Echo and Noise Control (IWAENC '01), September 2001, Darmstadt, Germany
Ikeda K, Sakamoto R: Convergence analyses of stereo acoustic echo cancelers with preprocessing. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 2003, 51(5):1324–1334. 10.1109/TSP.2003.810301
Benesty J, Huang Y (Eds): Adaptive Signal Processing: Applications to Real-World Problems. Springer, Berlin, Germany; 2003.
Sugiyama A, Hirano A, Nakayama K: Acoustic echo cancellation for conference systems. Proceedings of the European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO '04), September 2004, Vienna, Austria 17–20.
Buchner H, Benesty J, Kellermann W: Generalized multichannel frequency-domain adaptive filtering: efficient realization and application to hands-free speech communication. Signal Processing 2005, 85(3):549–570. 10.1016/j.sigpro.2004.07.029
Joncour Y, Sugiyama A: A stereo echo canceler with pre-processing for correct echo-path identification. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP '98), May 1998, Seattle, Wash, USA 6: 3677–3680.
Sugiyama A, Joncour Y, Hirano A: A stereo echo canceler with correct echo-path identification based on an input-sliding technique. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 2001, 49(11):2577–2587. 10.1109/78.960405
Ali M: Stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation system using time-varying all-pass filtering for signal decorrelation. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP '98), May 1998, Seattle, Wash, USA 6: 3689–3692.
Benesty J, Morgan DR, Hall JL, Sondhi MM: Stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation using nonlinear transformations and comb filtering. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP '98), May 1998, Seattle, Wash, USA 6: 3673–3676.
Gänsler T, Eneroth P: Influence of audio coding on stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP '98), May 1998, Seattle, Wash, USA 6: 3649–3652.
Gilloire A, Turbin V: Using auditory properties to improve the behaviour of stereophonic acoustic echo cancellers. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP '98), May 1998, Seattle, Wash, USA 6: 3681–3684.
Shimauchi S, Haneda Y, Makino S, Kaneda Y: New configuration for a stereo echo canceller with nonlinear pre-processing. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP '98), May 1998, Seattle, Wash, USA 6: 3685–3688.
Hirano A, Nakayama K, Watanabe K: Convergence analysis of stereophonic echo canceller with pre-processing—relation between pre-processing and convergence. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP '99), March 1999, Phoenix, Ariz, USA 2: 861–864.
Gänsler T, Benesty J: New insights into the stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation problem and an adaptive nonlinearity solution. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing 2002, 10(5):257–267. 10.1109/TSA.2002.800554
Yukawa M, Yamada I: Efficient adaptive stereo echo canceling schemes based on simultaneous use of multiple state data. IEICE Transactions on Fundamentals of Electronics, Communications and Computer Sciences 2004, E87-A(8):1949–1957.
Yamada I: Adaptive projected subgradient method: unified view for projection based adaptive algorithms. Journal of IEICE 2003, 86(8):654–658.
Yamada I, Ogura N: Adaptive projected subgradient method for asymptotic minimization of sequence of nonnegative convex functions. Numerical Functional Analysis and Optimization 2004, 25(7&8):593–617.
Cavalcante RLG, Yamada I, Sakaniwa K: A fast blind MAI reduction based on adaptive projected subgradient method. IEICE Transactions on Fundamentals of Electronics, Communications and Computer Sciences 2004, E87-A(8):1973–1980.
Yukawa M, Cavalcante RLG, Yamada I: Efficient blind MAI suppression in DS/CDMA systems by embedded constraint parallel projection techniques. IEICE Transactions on Fundamentals of Electronics, Communications and Computer Sciences 2005, E88-A(8):2062–2071. 10.1093/ietfec/e88-a.8.2062
Yamada I, Slavakis K, Yamada K: An efficient robust adaptive filtering algorithm based on parallel subgradient projection techniques. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 2002, 50(5):1091–1101. 10.1109/78.995065
Deutsch FR: Best Approximation in Inner Product Spaces. Springer, Berlin, Germany; 2001.
Censor Y, Zenios SA: Parallel Optimization: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications. Oxford University Press, New York, NY, USA; 1997.
Yukawa M, Yamada I: Acceleration of adaptive parallel projection algorithms by pairwise optimal weight realization. Proceedings of the 12th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO '04), September 2004, Vienna, Austria 713–716.
Yukawa M, Yamada I: Pairwise optimal weight realization—acceleration technique for set-theoretic adaptive parallel subgradient projection algorithm. 2005.https://doi.org/www.comm.ss.titech.ac.jp/~masahiro/publications.html) IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, accepted (For its preliminary version, see: Masahiro Yukawa and Isao Yamada, "On optimality of POWER weighting technique for adaptive filtering," Technical Report of IEICE, SIP2005-7, vol. 105, no. 29, pp.37–42, April 2005,
Hinamoto T, Maekawa S: Extended theory of learning identification. Transactions of the Institute of Electrical Engineers of Japan 1975, 95(10):227–234.
Ozeki K, Omeda T: An adaptive filtering algorithm using an orthogonal projection to an affine subspace and its properties. Transactions of IEICE 1984, 67-A(5):126–132.
Haykin S: Adaptive Filter Theory. 3rd edition. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA; 1996.
Sayed AH: Fundamentals of Adaptive Filtering. John Wiley & Sons, New York, NJ, USA; 2003.
Combettes PL: The foundations of set theoretic estimation. Proceedings of the IEEE 1993, 81(2):182–208.
Combettes PL: Convex set theoretic image recovery by extrapolated iterations of parallel subgradient projections. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 1997, 6(4):493–506. 10.1109/83.563316
Gollamudi S, Nagaraj S, Kapoor S, Huang YH: Set-membership filtering and a set-membership normalized LMS algorithm with an adaptive step size. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 1998, 5(5):111–114. 10.1109/97.668945
Guo L, Ekpenyong A, Huang YH: Frequency-domain adaptive filtering—a set-membership approach. Proceedings of the 37th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, November 2003, Pacific Grove, Calif, USA 2073–2077.
Bauschke HH, Borwein JM: On projection algorithms for solving convex feasibility problems. SIAM Review 1996, 38(3):367–426. 10.1137/S0036144593251710
Ogura N, Yamada I: A deep outer approximating half space of the level set of certain quadratic functions. Journal of Nonlinear and Convex Analysis 2005, 6(1):187–201.
Nagumo J, Noda A: A learning method for system identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 1967, 12(3):282–287.
Hassibi B, Sayed AH, Kailath T:
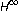 optimality of the LMS algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 1996, 44(2):267–280. 10.1109/78.485923
optimality of the LMS algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 1996, 44(2):267–280. 10.1109/78.485923Yukawa M, Yamada I: Adaptive parallel subgradient projection techniques with input sliding technique for stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation. in Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Workshop on Acoustic Echo and Noise Control (IWAENC '01), September 2003, Kyoto, Japan 55–58.
Gay SL: Dynamically regularized fast RLS with application to echo cancellation. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP '96), May 1996, Atlanta, Ga, USA 2: 957–960.
Gay SL, Tavathia S: The fast affine projection algorithm. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP '95), May 1995, Detroit, Mich, USA 5: 3023–3026.
Rupp M: A family of adaptive filter algorithms with decorrelating properties. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 1998, 46(3):771–775. 10.1109/78.661344
Tanaka M, Makino S, Kojima J: A block exact fast affine projection algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing 1999, 7(1):79–86. 10.1109/89.736333
Breining C, Dreiseitel P, Hänsler E, et al.: Acoustic echo control. An application of very-high-order adaptive filters. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 1999, 16(4):42–69. 10.1109/79.774933
Sankaran SG, Beex AA(Louis): Convergence behavior of affine projection algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 2000, 48(4):1086–1096. 10.1109/78.827542
Botto J-L, Moustakides GV: Stabilizing the fast Kalman algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing 1989, 37(9):1342–1348. 10.1109/29.31289
Moustakides GV: Correcting the instability due to finite precision of the fast Kalman identification algorithms. Signal Processing 1989, 18: 33–42. 10.1016/0165-1684(89)90060-1
Slock DTM, Kailath T: Numerically stable fast transversal filters for recursive least squares adaptive filtering. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 1991, 39(1):92–114. 10.1109/78.80769
Glentis G-O, Berberidis K, Theodoridis S: A unified view—efficient least squares adaptive algorithms for FIR transversal filtering. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 1999, 16(4):13–41. 10.1109/79.774932
Haykin S, Sayed AH, Zeidler JR, Yee P, Wei PC: Adaptive tracking of linear time-variant systems by extended RLS algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 1997, 45(5):1118–1128. 10.1109/78.575687
Leung S-H, So CF: Gradient-based variable forgetting factor RLS algorithm in time-varying environments. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 2005, 53(8):3141–3150.
Sankaran SG, Beex AA(Louis): Stereophonic echo cancellation using NLMS with orthogonal correction factors. Proceedings of the International Workshop on Acoustic Echo and Noise Control (IWAENC '99), September 1999, Pocono Manor, Pa, USA 40–43.
Lai J-T, Wu A-Y, Yeh C-C: A novel multipath matrix algorithm for exact room response identification in stereo echo cancellation. Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Signal Processing Systems (SIPS '03), August 2003, Seoul, Korea 236–240.
Hirano A, Nakayama K, Someda D, Tanaka M: Stereophonic acoustic echo canceller without pre-processing. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP '04), May 2004, Montreal, Canada 4: 145–148.
Khong AWH, Naylor PA: Reducing inter-channel coherence in stereophonic acoustic echo cancellation using partial update adaptive filters. Proceedings of the European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO '04), September 2004, Vienna, Austria 405–408.
Morgan DR, Hall JL, Benesty J: Investigation of several types of nonlinearities for use in stereo acoustic echo cancellation. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing 2001, 9(6):686–696. 10.1109/89.943346
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Yukawa, M., Murakoshi, N. & Yamada, I. Efficient Fast Stereo Acoustic Echo Cancellation Based on Pairwise Optimal Weight Realization Technique. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2006, 084797 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1155/ASP/2006/84797
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/ASP/2006/84797
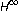 optimality of the LMS algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 1996, 44(2):267–280. 10.1109/78.485923
optimality of the LMS algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 1996, 44(2):267–280. 10.1109/78.485923