- Research Article
- Published:
Analysis and Synthesis of Pseudo-Periodic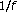 -Like Noise by Means of Wavelets with Applications to Digital Audio
-Like Noise by Means of Wavelets with Applications to Digital Audio
EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing volume 2001, Article number: 584201 (2001)
Abstract
Voiced musical sounds have nonzero energy in sidebands of the frequency partials. Our work is based on the assumption, often experimentally verified, that the energy distribution of the sidebands is shaped as powers of the inverse of the distance from the closest partial. The power spectrum of these pseudo-periodic processes is modeled by means of a superposition of modulated components, that is, by a pseudo-periodic
components, that is, by a pseudo-periodic -like process. Due to the fundamental selfsimilar character of the wavelet transform,
-like process. Due to the fundamental selfsimilar character of the wavelet transform, processes can be fruitfully analyzed and synthesized by means of wavelets. We obtain a set of very loosely correlated coefficients at each scale level that can be well approximated by white noise in the synthesis process.
processes can be fruitfully analyzed and synthesized by means of wavelets. We obtain a set of very loosely correlated coefficients at each scale level that can be well approximated by white noise in the synthesis process.
Our computational scheme is based on an orthogonal -band filter bank and a dyadic wavelet transform per channel. The
-band filter bank and a dyadic wavelet transform per channel. The channels are tuned to the left and right sidebands of the harmonics so that sidebands are mutually independent. The structure computes the expansion coefficients of a new orthogonal and complete set of harmonic-band wavelets. The main point of our scheme is that we need only two parameters per harmonic in order to model the stochastic fluctuations of sounds from a pure periodic behavior.
channels are tuned to the left and right sidebands of the harmonics so that sidebands are mutually independent. The structure computes the expansion coefficients of a new orthogonal and complete set of harmonic-band wavelets. The main point of our scheme is that we need only two parameters per harmonic in order to model the stochastic fluctuations of sounds from a pure periodic behavior.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Polotti, P., Evangelista, G. Analysis and Synthesis of Pseudo-Periodic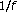 -Like Noise by Means of Wavelets with Applications to Digital Audio.
EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2001, 584201 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1155/S1110865701000129
-Like Noise by Means of Wavelets with Applications to Digital Audio.
EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2001, 584201 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1155/S1110865701000129
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/S1110865701000129