- Research Article
- Open access
- Published:
Nearest Neighborhood Grayscale Operator for Hardware-Efficient Microscale Texture Extraction
EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing volume 2007, Article number: 052630 (2006)
Abstract
First-stage feature computation and data rate reduction play a crucial role in an efficient visual information processing system. Hardware-based first stages usually win out where power consumption, dynamic range, and speed are the issue, but have severe limitations with regard to flexibility. In this paper, the local orientation coding (LOC), a nearest neighborhood grayscale operator, is investigated and enhanced for hardware implementation. The features produced by this operator are easy and fast to compute, compress the salient information contained in an image, and lend themselves naturally to various medium-to-high-level postprocessing methods such as texture segmentation, image decomposition, and feature tracking. An image sensor architecture based on the LOC has been elaborated, that combines high dynamic range (HDR) image aquisition, feature computation, and inherent pixel-level ADC in the pixel cells. The mixed-signal design allows for simple readout as digital memory.
References
Tongprasit B, Ito K, Shibata T: A computational digital-pixel-sensor VLSI featuring block-readout architecture for pixel-parallel rank-order filtering. Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS '05), May 2005, Kobe, Japan 3: 2389–2392.
Elouardi A, Bouaziz S, Dupret A, Klein JO, Reynaud R: Image processing vision system implementing a smart sensor. Proceedings of the 21st IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (IMTC '04), May 2004, Como, Italy 1: 445–450.
Massari N, Gottardi M, Gonzo L, Stoppa D, Simoni A: A CMOS image sensor with programmable pixel-level analog processing. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 2005,16(6):1673–1684. 10.1109/TNN.2005.854369
Zitová B, Kautsky J, Peters G, Flusser J: Robust detection of significant points in multiframe images1. Pattern Recognition Letters 1999,20(2):199–206. 10.1016/S0167-8655(98)00135-4
König A, Mayr C, Bormann T, Klug C: Dedicated implementation of embedded vision systems employing low-power massively parallel feature computation. Proceedings of the 3rd VIVA-Workshop on Low-Power Information Processing, March 2002, Chemnitz, Germany 1–8.
Rüedi P-F, Heim P, Kaess F, et al.:A
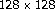 pixel 120-dB dynamic-range vision-sensor chip for image contrast and orientation extraction. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 2003,38(12):2325–2333. 10.1109/JSSC.2003.819169
pixel 120-dB dynamic-range vision-sensor chip for image contrast and orientation extraction. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 2003,38(12):2325–2333. 10.1109/JSSC.2003.819169Goerick C, Brauckmann M: Local orientation coding and neural network classifiers with an application to real time car detection and tracking. In Proceedings of the 16th Symposium of the DAGM and the 18th Workshop of the ÖAGM, 1994, New York, NY, USA. Edited by: Kropatsch W, Bischof H. Springer;
König A, Eberhardt M, Wenzel R: A transparent and flexible development environment for rapid design of cognitive systems. Proceedings of 24th Euromicro Conference, August 1998, Vasteras, Sweden 2: 655–662.
Günther A: Design of a library of scalable, low-power CMOS cells for classification and feature extraction in integrated cognition systems, Diploma thesis.
Minch BA: Analysis and synthesis of static translinear circuits. In Tech. Rep. CSL-TR-2000-1002. Computer Systems Laboratory, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA; 2000.
Raffo L: Analysis and synthesis of resistive networks for distributed visual elaborations. Electronics Letters 1996,32(8):743–744. 10.1049/el:19960484
Mayr C: Current scaling in current-mode CMOS circuits. Proceedings of Dresdner Arbeitstagung Schaltungs- und Systementwurf (DASS '05), April 2005, Dresden, Germany 91–96.
Mayr C, Schueffny R: Image pulse coding scheme applied to feature extraction. Proceedings Image and Vision Computing New Zealand (IVCNZ '05), November 2005, Dunedin, New Zealand 49–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Mayr, C., König, A. Nearest Neighborhood Grayscale Operator for Hardware-Efficient Microscale Texture Extraction. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2007, 052630 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/52630
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/52630
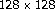 pixel 120-dB dynamic-range vision-sensor chip for image contrast and orientation extraction. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 2003,38(12):2325–2333. 10.1109/JSSC.2003.819169
pixel 120-dB dynamic-range vision-sensor chip for image contrast and orientation extraction. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 2003,38(12):2325–2333. 10.1109/JSSC.2003.819169