- Research Article
- Open access
- Published:
Geometric Properties of Grassmannian Frames for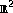 and
and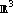
EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing volume 2006, Article number: 049850 (2006)
Abstract
Grassmannian frames are frames satisfying a min-max correlation criterion. We translate a geometrically intuitive approach for two- and three-dimensional Euclidean space ( and
and ) into a new analytic method which is used to classify many Grassmannian frames in this setting. The method and associated algorithm decrease the maximum frame correlation, and hence give rise to the construction of specific examples of Grassmannian frames. Many of the results are known by other techniques, and even more generally, so that this paper can be viewed as tutorial. However, our analytic method is presented with the goal of developing it to address unresovled problems in
) into a new analytic method which is used to classify many Grassmannian frames in this setting. The method and associated algorithm decrease the maximum frame correlation, and hence give rise to the construction of specific examples of Grassmannian frames. Many of the results are known by other techniques, and even more generally, so that this paper can be viewed as tutorial. However, our analytic method is presented with the goal of developing it to address unresovled problems in -dimensional Hilbert spaces which serve as a setting for spherical codes, erasure channel modeling, and other aspects of communications theory.
-dimensional Hilbert spaces which serve as a setting for spherical codes, erasure channel modeling, and other aspects of communications theory.
References
Christensen O: An Introduction to Frames and Riesz Bases. Birkhäuser, Boston, Mass, USA; 2002.
Strohmer T, Heath RW Jr.: Grassmannian frames with applications to coding and communication. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis 2003, 14(3):257–275. 10.1016/S1063-5203(03)00023-X
Benedetto JJ, Fickus M: Finite normalized tight frames. Advances in Computational Mathematics 2003, 18(2–4):357–385.
Conway JH, Hardin RH, Sloane NJA: Packing lines, planes, etc.: packings in Grassmannian spaces. Experimental Mathematics 1996, 5(2):139–159.
Eldar YC, Bölcskei H: Geometrically uniform frames. IEEE Transactions on Informormation Theory 2003, 49(4):993–1006. 10.1109/TIT.2003.809602
Tropp JA, Dhillon IS, Heath RW Jr., Strohmer T: Designing structured tight frames via an alternating projection method. IEEE Transactions on Informormation Theory 2005, 51(1):188–209.
Goyal VK, Kovačević J, Kelner JA: Quantized frame expansions with erasures. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis 2001, 10(3):203–233. 10.1006/acha.2000.0340
Casazza PG, Kovačević J: Equal-norm tight frames with erasures. Advances in Computational Mathematics 2003, 18(2–4):387–430.
Holmes R, Paulsen V: Optimal frames for erasures. Linear Algebra and its Applications 2004, 377(1):31–51.
Fejes Tóth L: Distribution of points in the elliptic plane. Acta Mathematica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae 1965, 16: 437–440. 10.1007/BF01904849
Lay DC: Linear Algebra and Its Applications. Addison-Wesley, Boston, Mass, USA; 2003.
Duffin RJ, Schaeffer AC: A class of nonharmonic Fourier series. Transactions of the American Mathematical Society 1952, 72(2):341–366. 10.1090/S0002-9947-1952-0047179-6
Benedetto JJ, Frazier MW (Eds): Wavelets: Mathematics and Applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fla, USA; 1994.
Daubechies I: Ten Lectures on Wavelets. SIAM, Philadelphia, Pa, USA; 1992.
Rosenfeld M: In praise of the Gram matrix. In The Mathematics of Paul Erdős, II, Algorithms and Combinatorics. Volume 14. Springer, Berlin, Germany; 1997:318–323.
Welch LR: Lower bounds on the maximum cross-correlation of signals. IEEE Transactions on Informormation Theory 1974, 20(3):397–399. 10.1109/TIT.1974.1055219
Panik MJ: Fundamentals of Convex Analysis: Duality, Separation, Representation, and Resolution. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, the Netherlands; 1993.
Lay SR: Convex Sets and Their Applications. John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, USA; 1982.
Webster R: Convexity. Oxford University Press, New York, NY, USA; 1994.
Krein M, Milman D: On extreme points of regular convex sets. Studia Mathematica 1940, 9: 133–138.
Lemmens PWH, Seidel JJ: Equiangular lines. Journal of Algebra 1973, 24(3):494–512. 10.1016/0021-8693(73)90123-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Benedetto, J.J., Kolesar, J.D. Geometric Properties of Grassmannian Frames for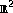 and
and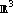 .
EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2006, 049850 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1155/ASP/2006/49850
.
EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2006, 049850 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1155/ASP/2006/49850
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/ASP/2006/49850